CMU 11611 的课程笔记。关于 Treebank,parsing algorithm,advanced grammar,这一章介绍的非常简略,以后会补充。
Treebank
来考虑一下 production rules 是怎么产生的,过去很长一段时间用的都是 hand-written grammars,需要专家编写,很难 scale,覆盖率也非常有限,所以人们手工建立了 treebank,也就是对某些语料集做的标注(annotated data),之后 production rules 就可以通过算法直接从 treebank 抽取。
E.g.
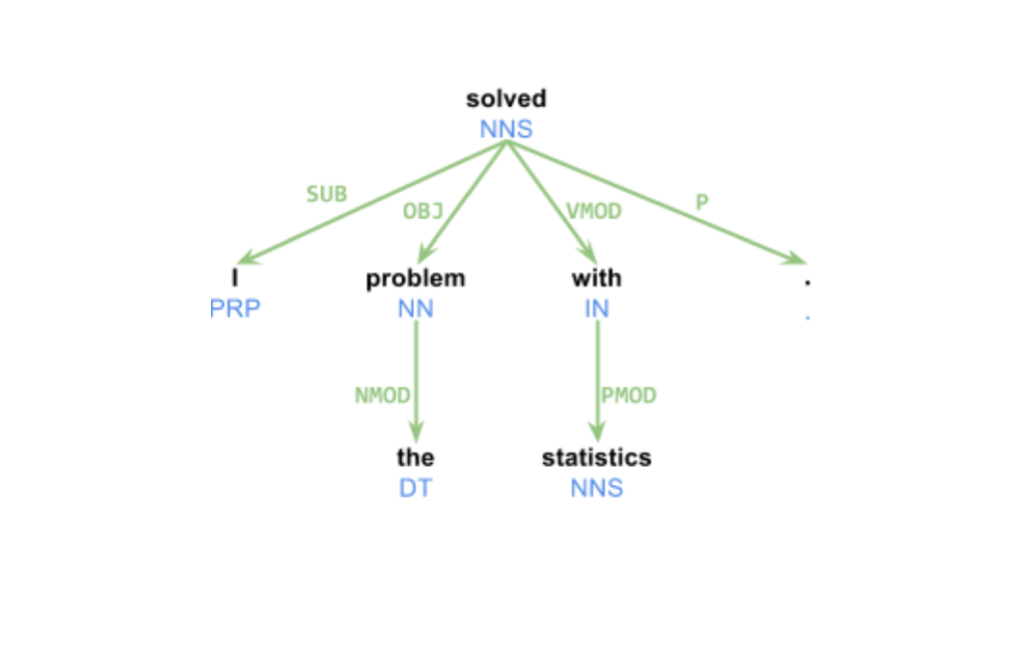
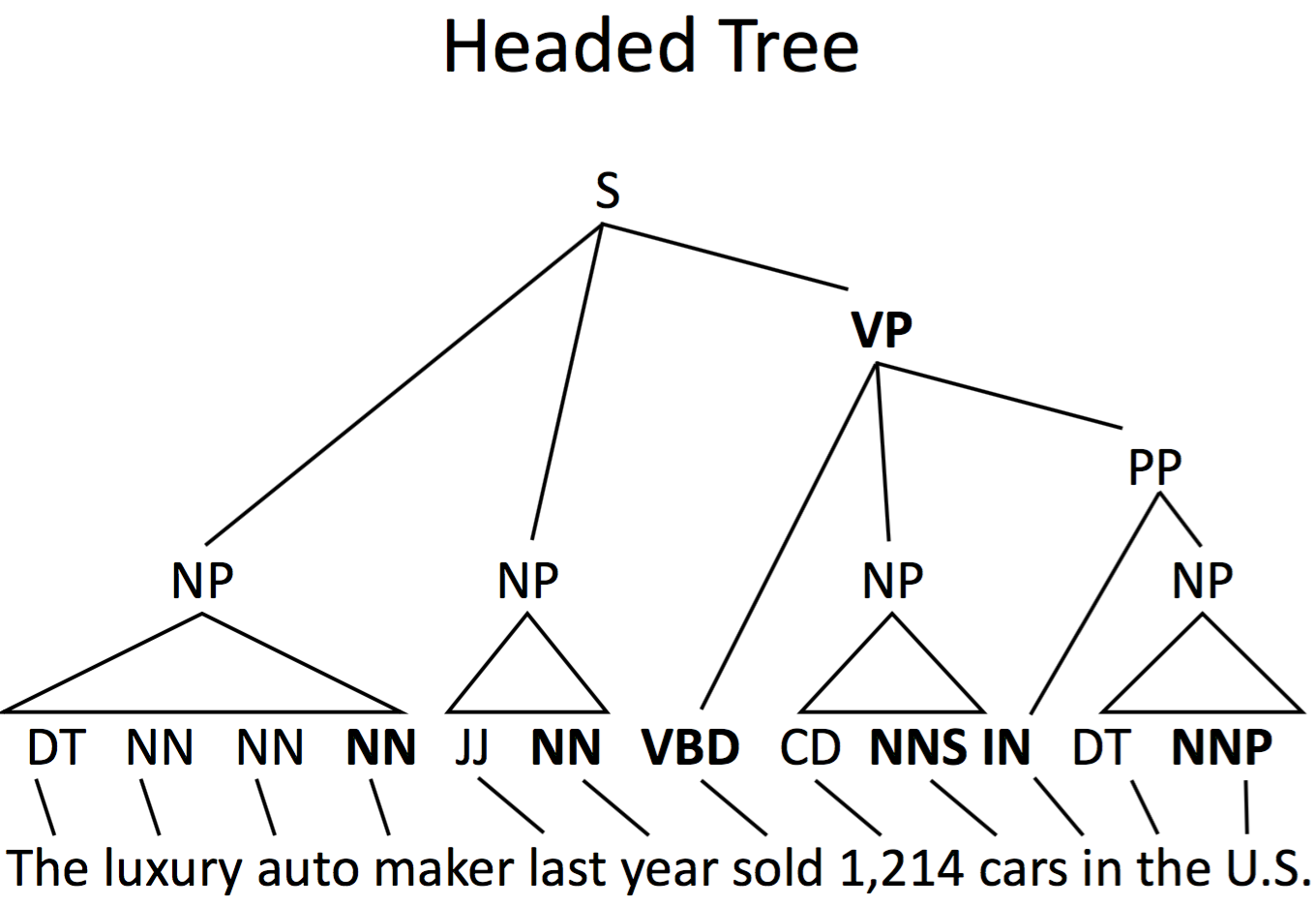
利用 Head rules,我们可以将 Penn Treebank tree 自动转化为一个 dependency tree,一些规则如下:
优势
- Reusability of the labor
- Many parsers, POS taggers, etc.
一个 treebank 包含了很多种信息,可以用于多种 parser - Valuable resource for linguistics
- Broad coverage
Penn Treebank 包含了多个语料库(Brown Corpus/Wall Street Journal/ATIS/Switchboard),每个语料库有大约一百万的单词,覆盖很广 - Frequencies and distributional information
包含了 frequency 信息 - Use Machine Learning algorithms to train parsers
把 treebank 数据分为 training set/dev set/test set,来训练 parser 吧~ - A way to evaluate systems
可以用来评估 parser 效果
问题
最大的一个问题是 too big to fail。因为建立这些 treebank 很费时费力费钱,所以它们不能轻易的被替代;另外,尽管大多数的决定是由专家来做的,然而大多数的 coding 确是由非专家来完成的,而这些人也处于高压以及有限预算下,treebank 并不是尽善尽美的。
Treebank Dataset
The Prague Dependency Treebanks: Extremely high quality
The Google Universal Dependency Treebanks
Tools
Tregex
T-Regex operators
T-surgeon
Dependency Parsing
- Dynamic programming (CFG with heads + CKY)
和 lexicalized PCFG parsing 类似
时间复杂度:O(n^5)
Eisner (1996) 提出一种 O(n^3) 的算法, 在结束的时候再产生 items with heads 而不是在中间产生 - Graph algorithms
McDonald et al.’s (2005) MSTParser(Maximum Spanning Tree), 单独用 ML 分类器来给 dependencies 算分 - Constraint Satisfaction
Karlsson (1990), etc. 建立所有 links, 然后删掉不符合 hard constraints 的 link - “Deterministic parsing”
Nivre et al. (2008): MaltParser, Greedy choice of aKachments guided by ML classifiers
实现 Dependency Parsing 主要要解决 linking 和 shifting 的问题,通常可以用机器学习分类器来解决
Source of information/Features:
- Bilexical affinities
issues→the is plausible - Dependency distance
mostly short links - Intervening material
Dependencies rarely span intervening verbs or punctuation - Valency of heads
How many dependents on which side are usual for a head? - Some lexical word links are more common
MaltParser
有时间再回来填坑
Dependency Parsing
Advanced Grammars
- Standard CFG
- Lexicalized Grammars
- Other formalisms
Tree Adjoining Grammars
Unification Grammars
Categorial Grammars
Tree Adjoining Grammars(TAG)
TAG 是一个改写树的系统(formal tree rewriting system)
Basics of TAG Formalism
- Primitive elements: elementary trees
Initial trees
Auxiliary trees - Operations
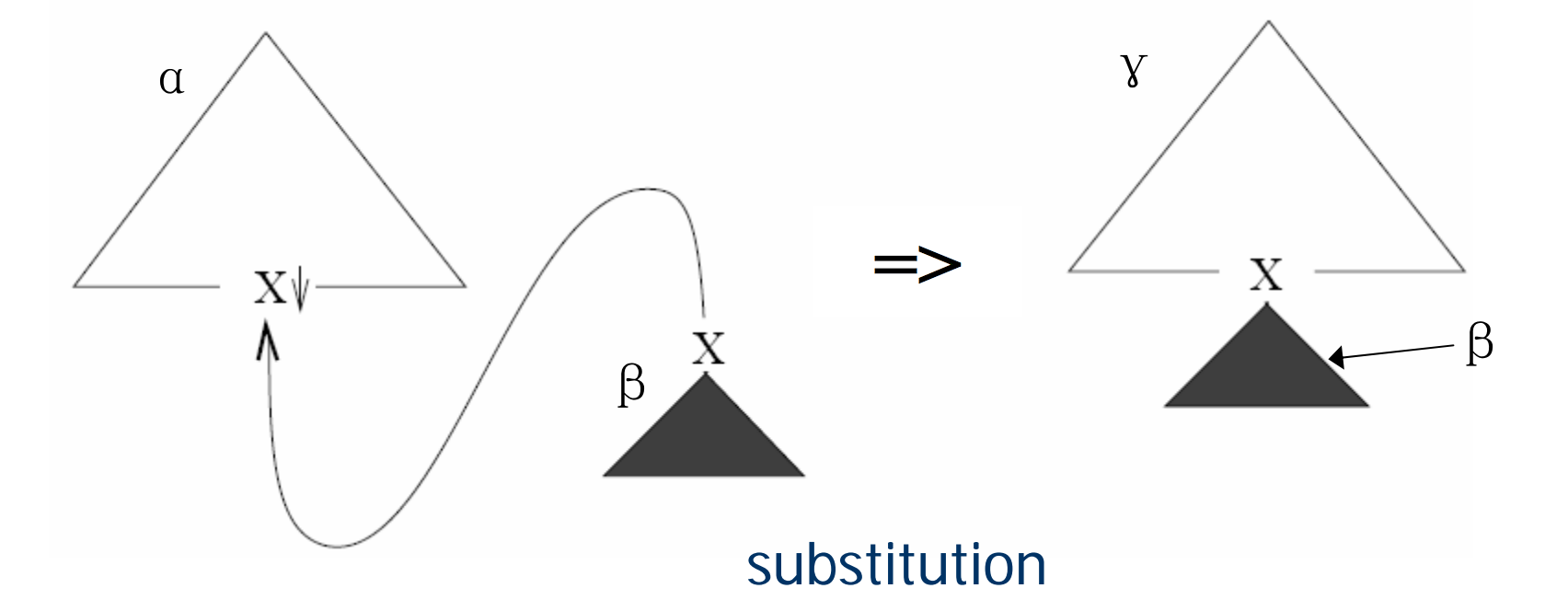
Substitution
Adjoining - Derivations
Derived trees
Derivation trees
TAG 是 CFG 的一个局部域,一级树(One level tree)对应一条规则,不是每条规则都要词汇化(lexicalized)。
Is a grammar capable of
- Lexicalization of each elementary domain
- Encapsulation of the arguments of the lexical anchor
Elementary trees
至少包括了一个边界节点(frontier node)是 terminal 符号,或者我们说是 lexical anchor。
Initial tree & Substitution
- 所有内部节点(interior nodes)是 non-terminal 符号
- 边界节点(frontier node)是 terminal/non-terminal 符号,用来替换,标记为↓
E.g.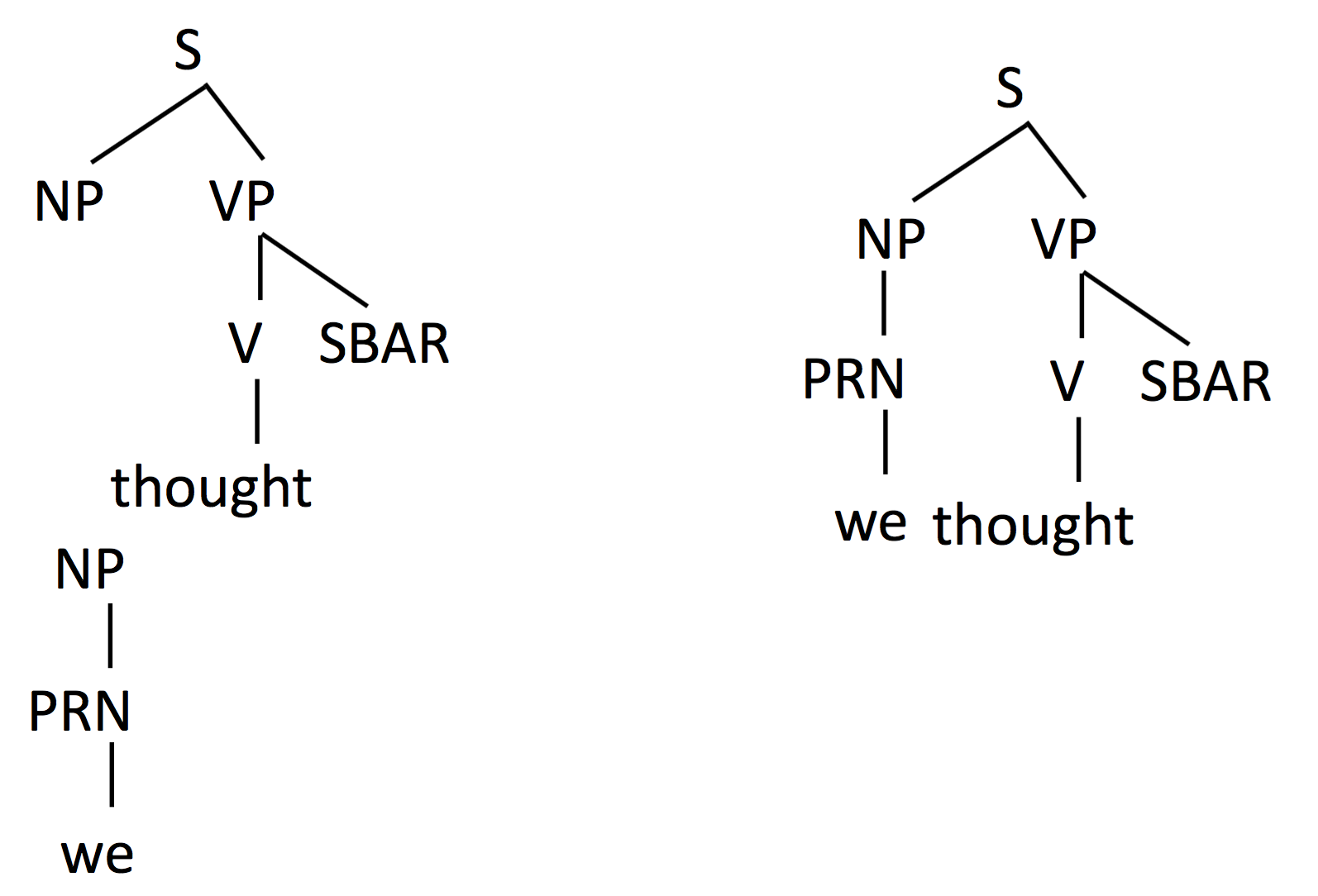
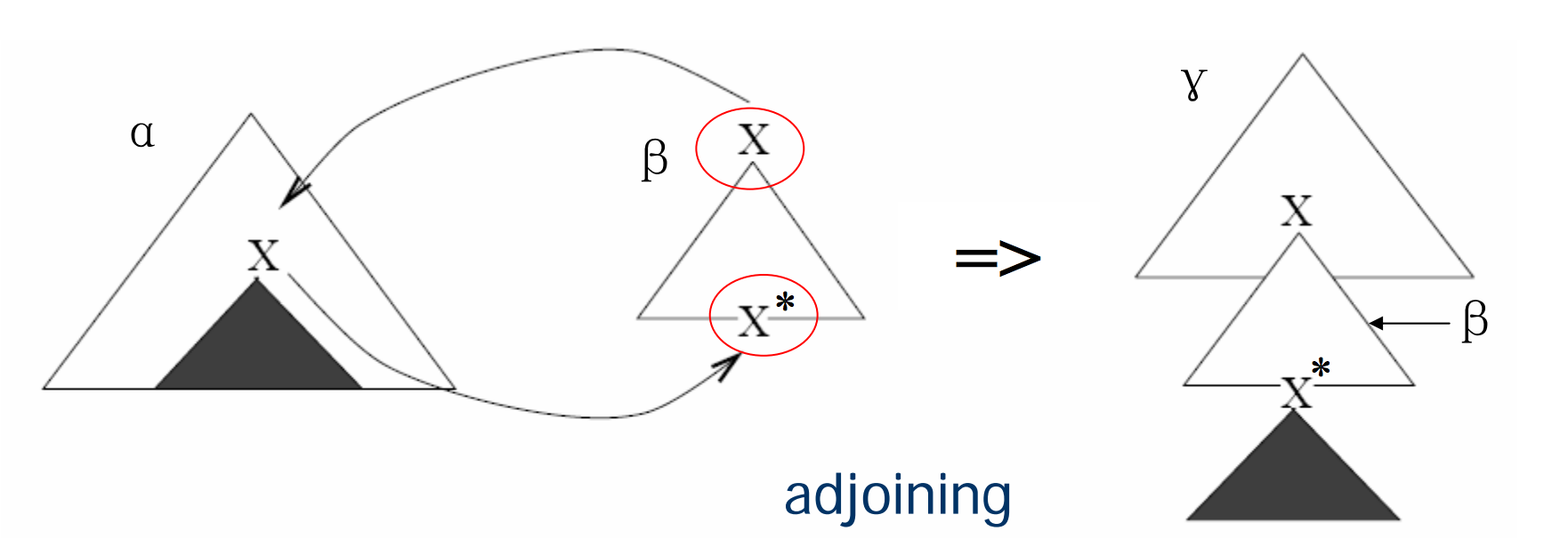
Auxiliary Trees & Adjoining
- 有一个边界节点(frontier node)必须被标记为 foot node(*)
- 这个 foot node 必须是 non-terminal 符号,并且和根节点(root node)相同
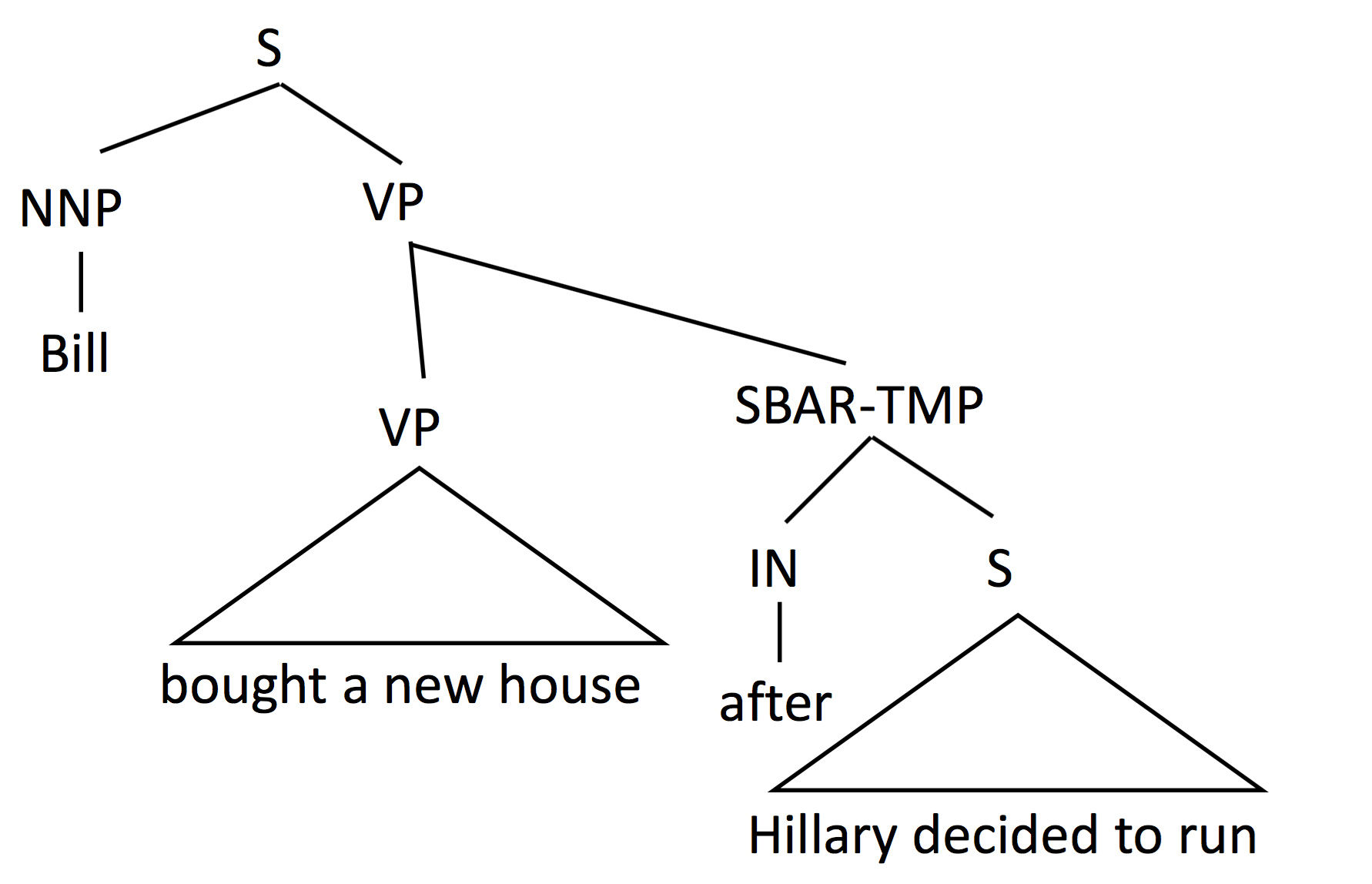
E.g.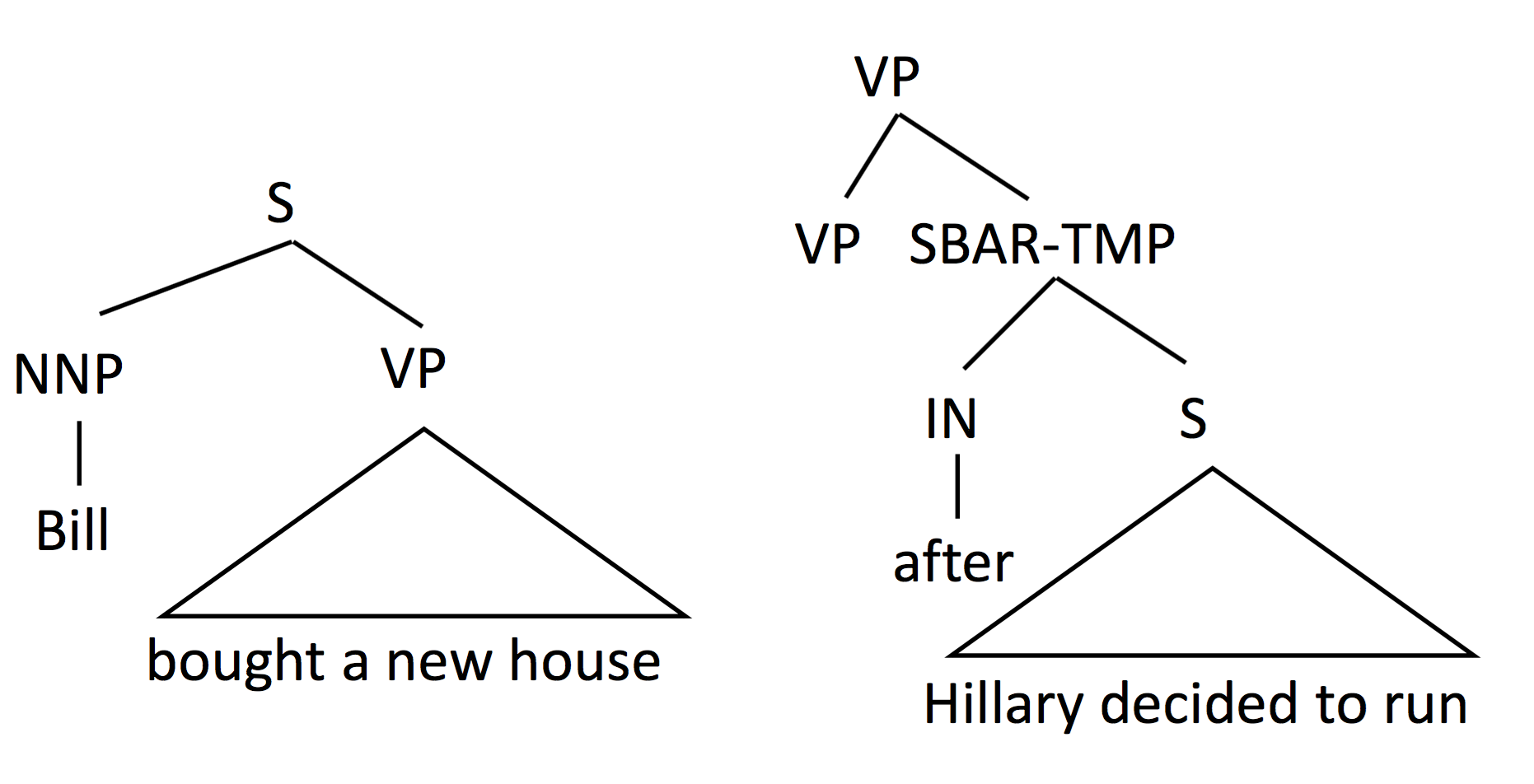
An Introduction to
Tree Adjoining Grammars
Unification Grammars
Unification Grammars 主要用于解决 一致性(agreement)问题,希望不用重复执行 NP-single 和 NP-plural 的 NP 规则
|
|
貌似要研究一下 feature structure,参考Unification Grammars
Categorial Grammars(CCG)
大多数的 CCG 是从成分角度来分析句子结构的,所以它们是 phrase structure grammars
基本的 5 条规则:
- A/B + B = A
- B + A\B = A
- A/B + B/C = A/C
- A CONJ A’ = A
- A = X/(X\A)
Forward: X/Y Y => X X 后面如果接 Y,那么这个 phrase 就变成 X
Backward: Y X\Y => X X 前面如果是 Y,那么这个 phrase 就变成 X
E.g.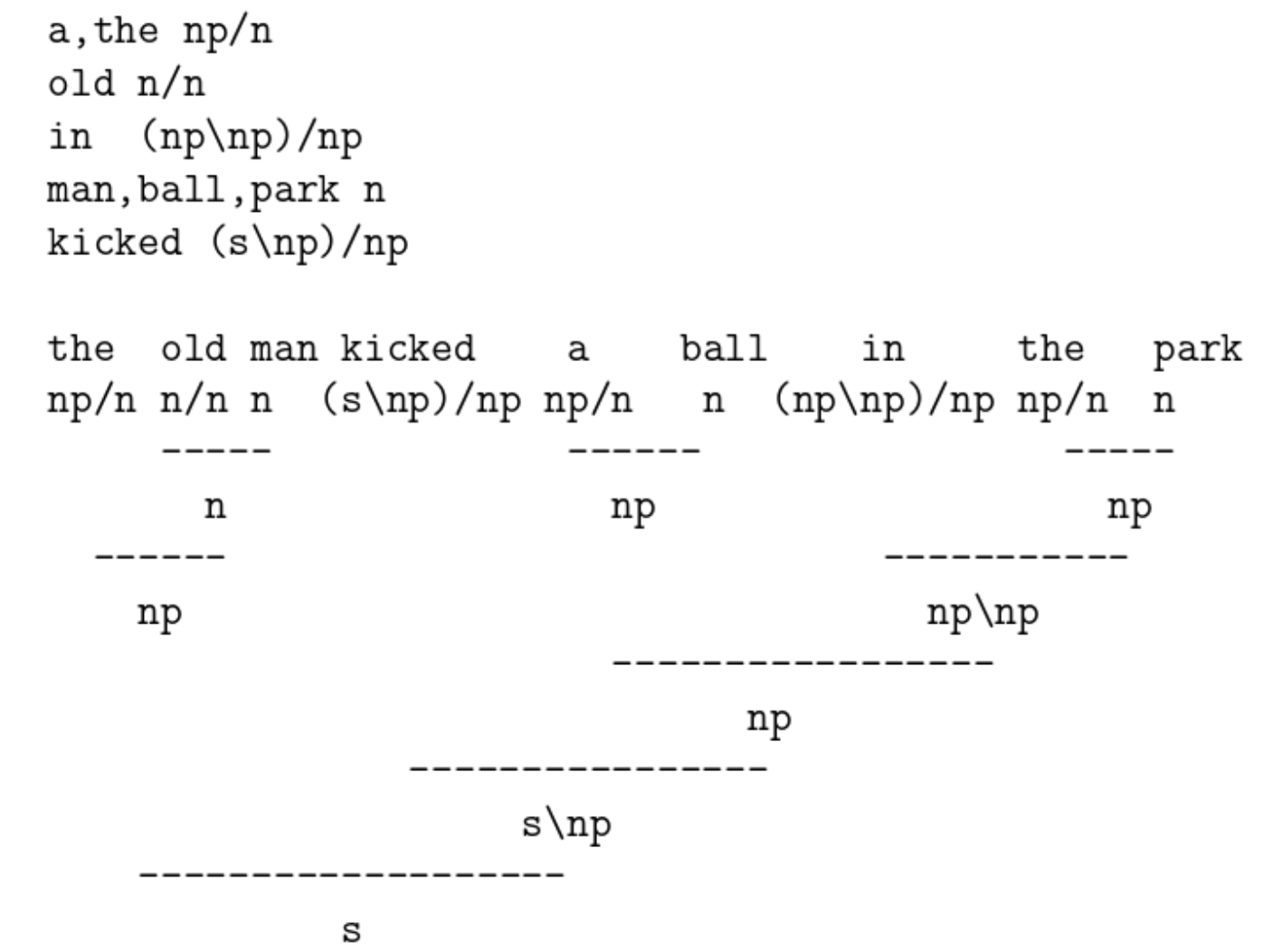
Dependency vs Constituent
可以通过 head rules 来从 CFG 中得到 dependency parse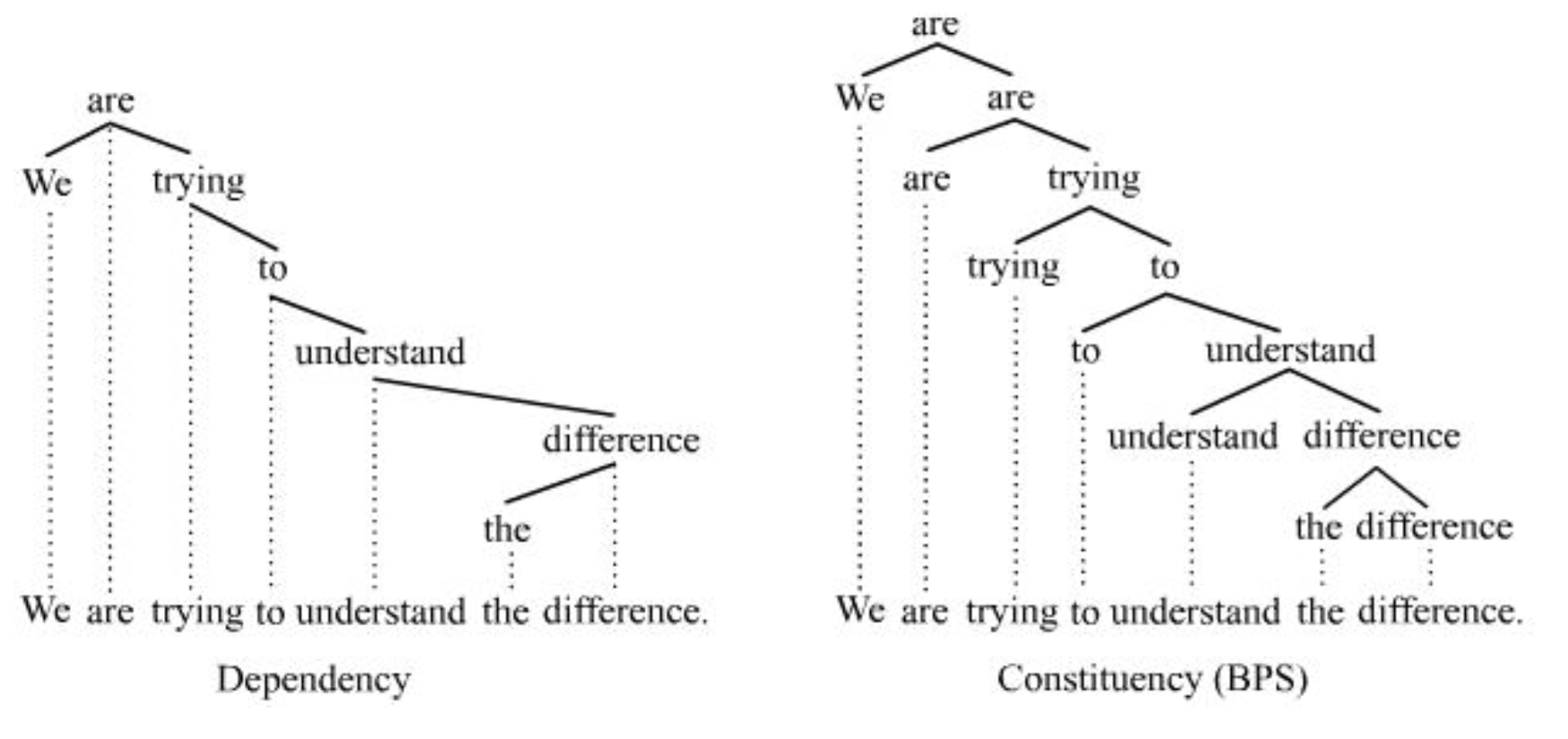
CT → DT 要比 DT → CT 简单多了。
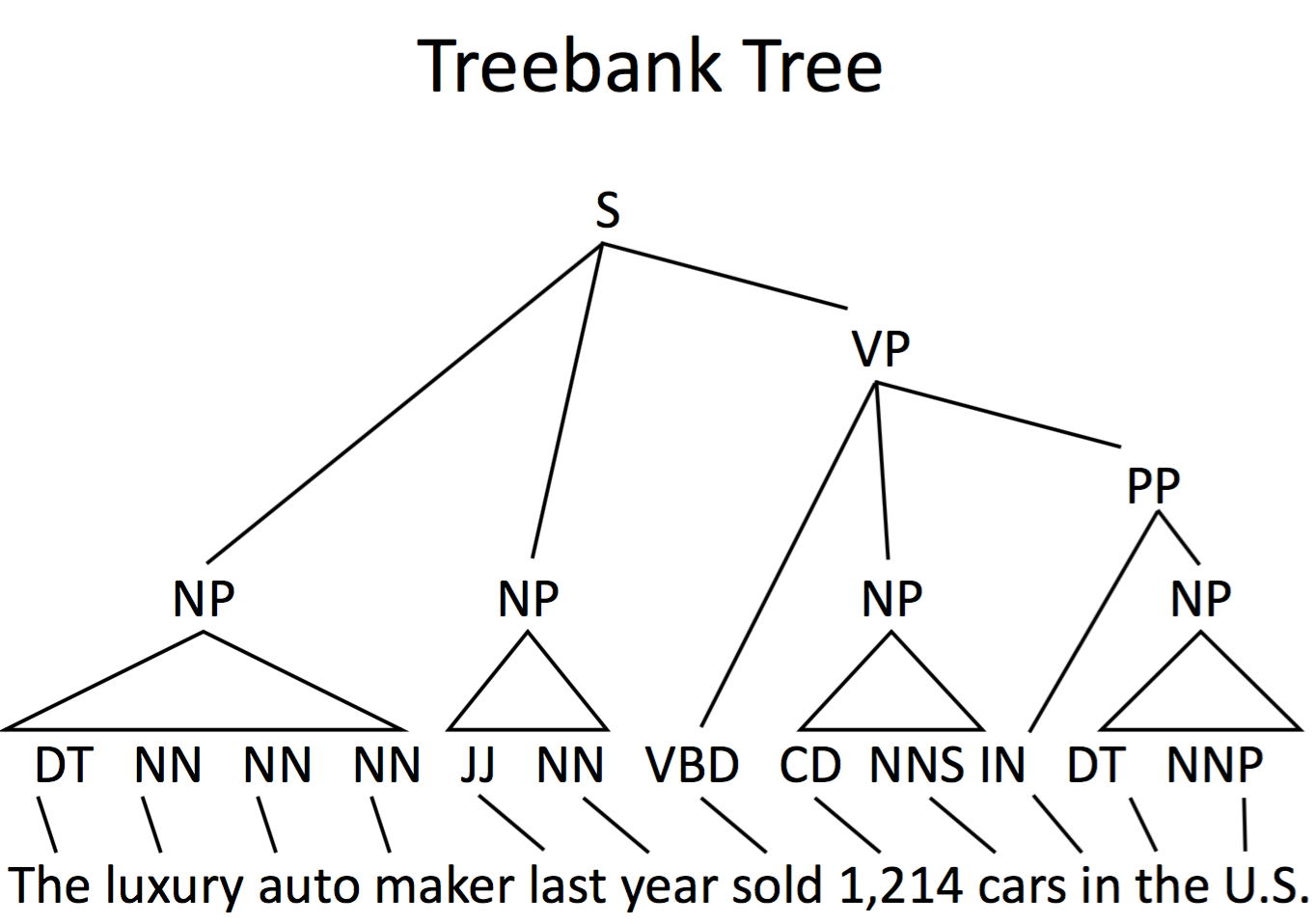
Tree Example
Treebank Tree
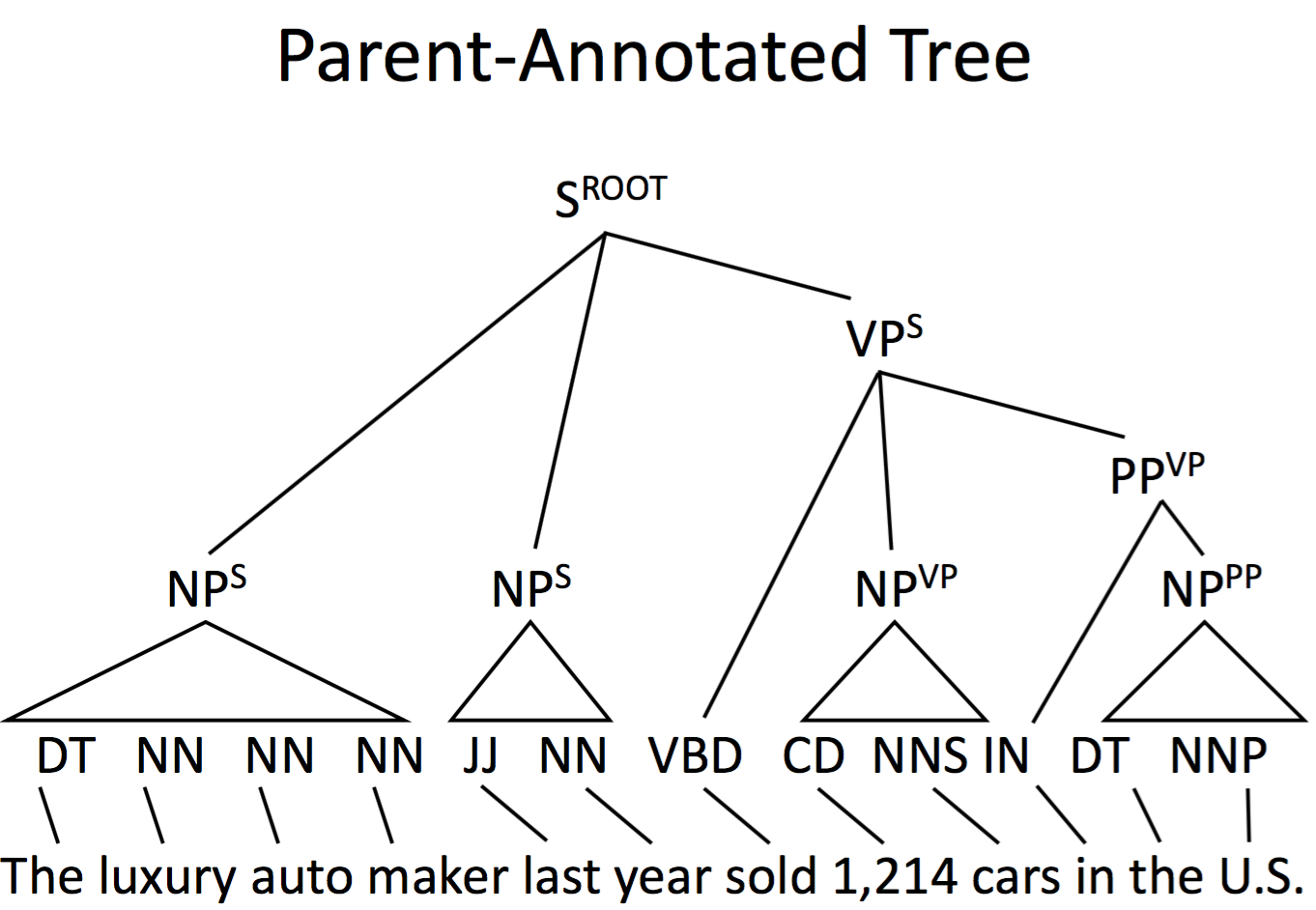
Parent-Annotated Tree
Headed Tree
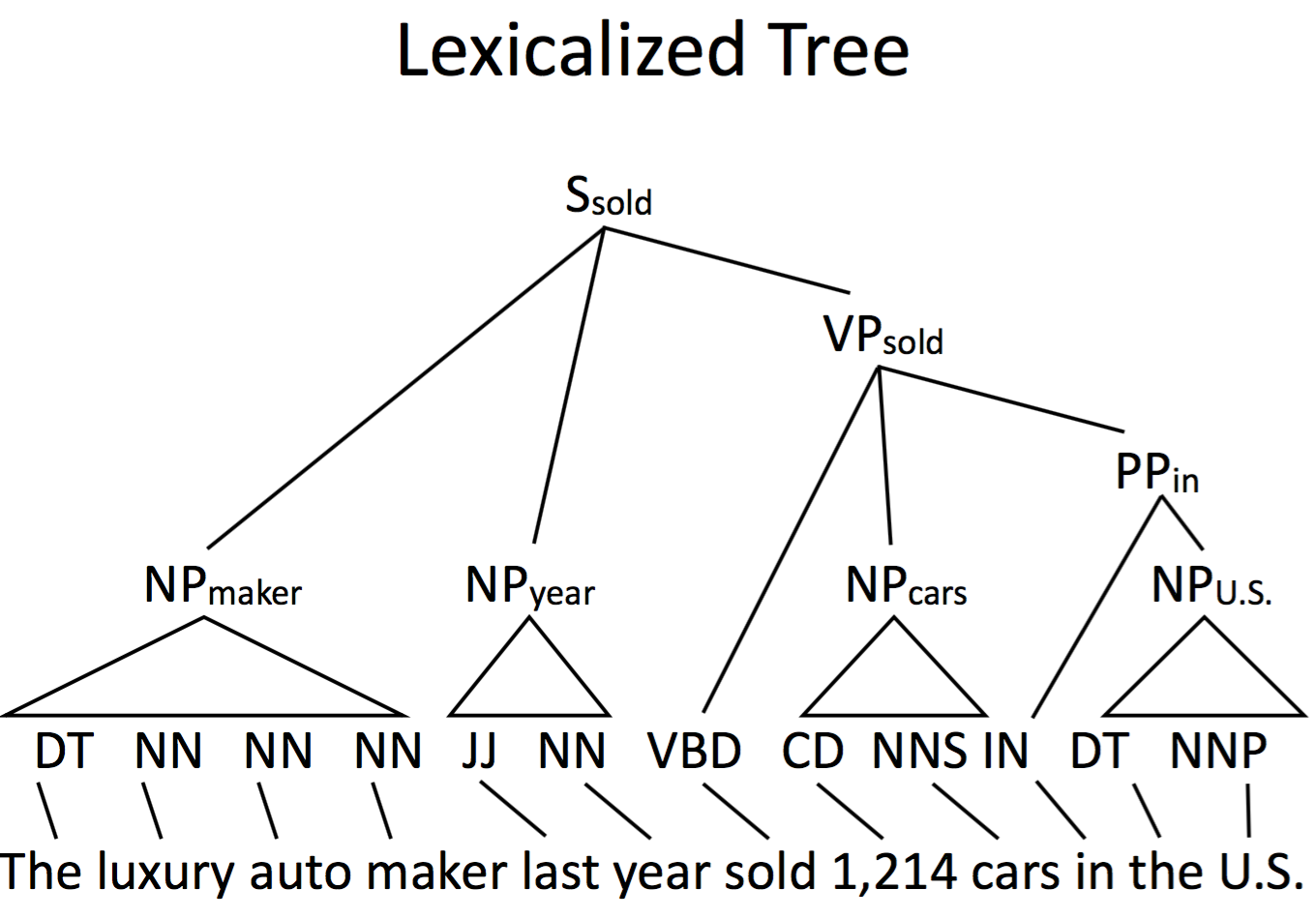
Lexicalized Tree